
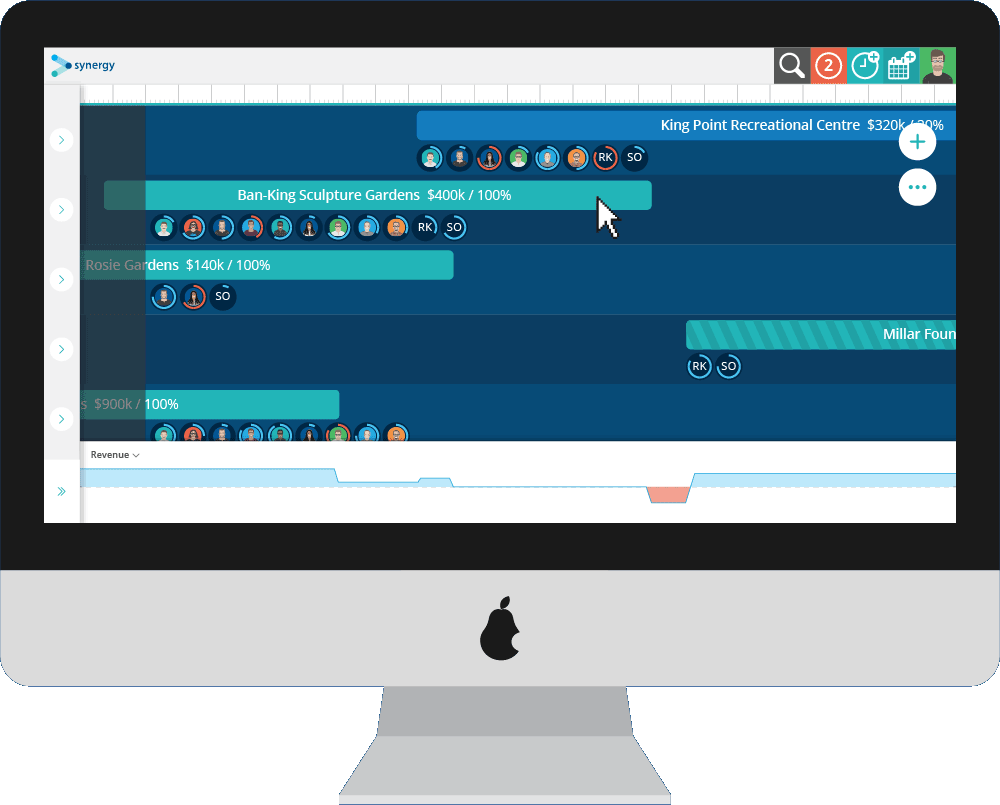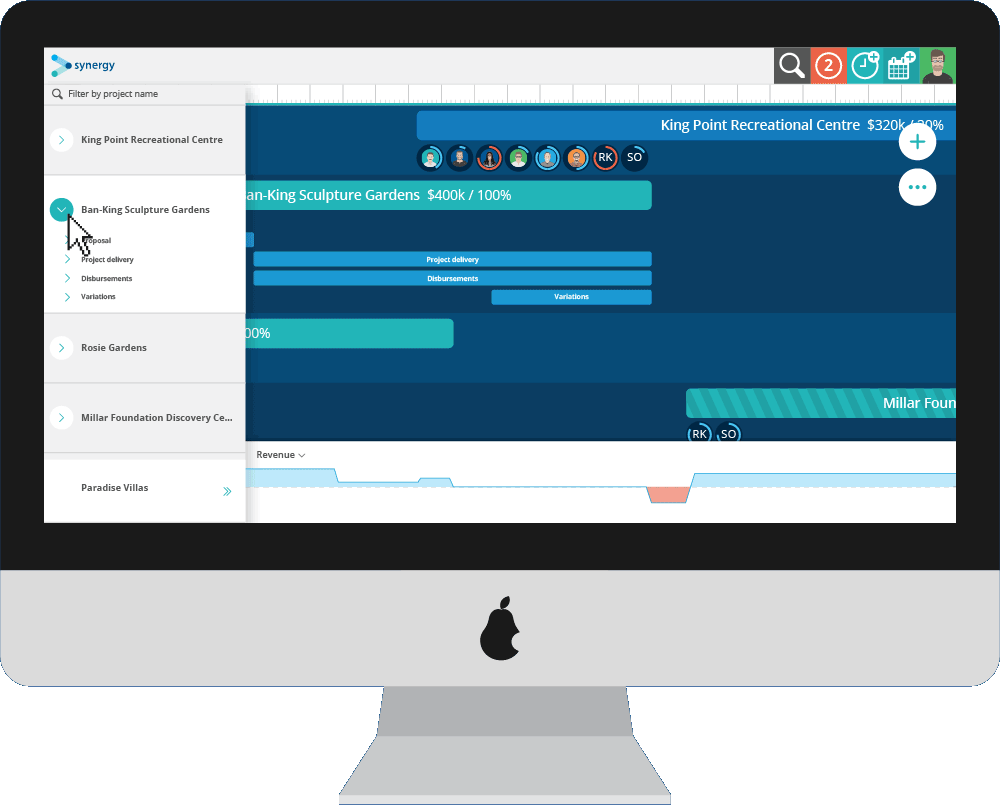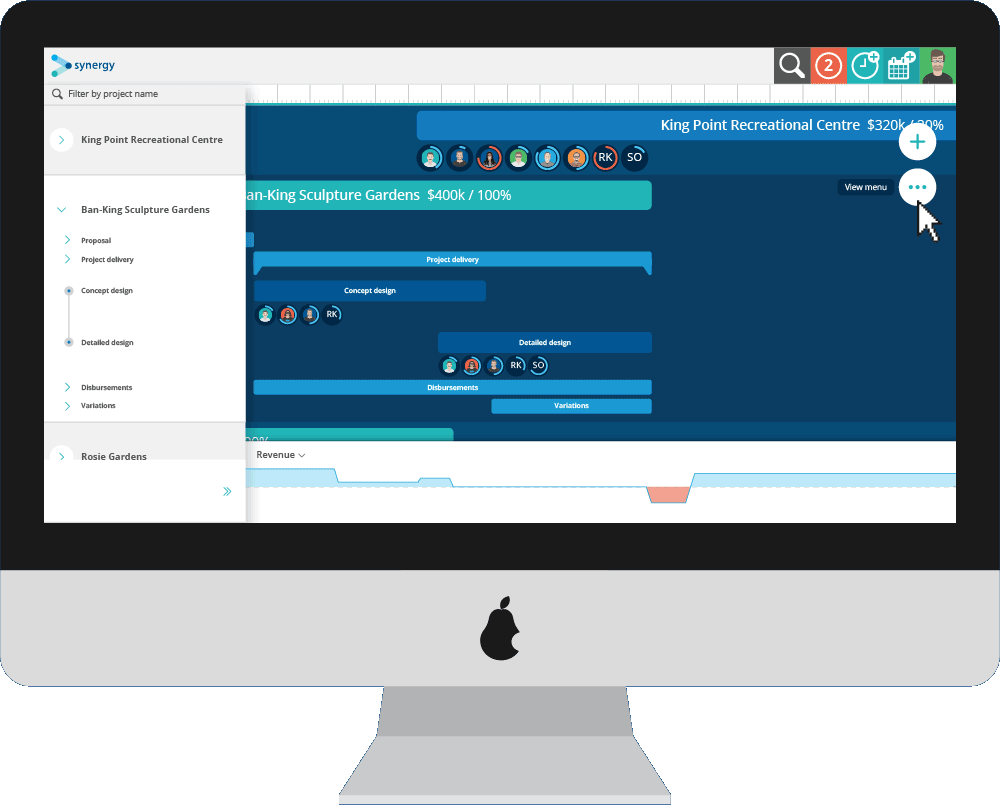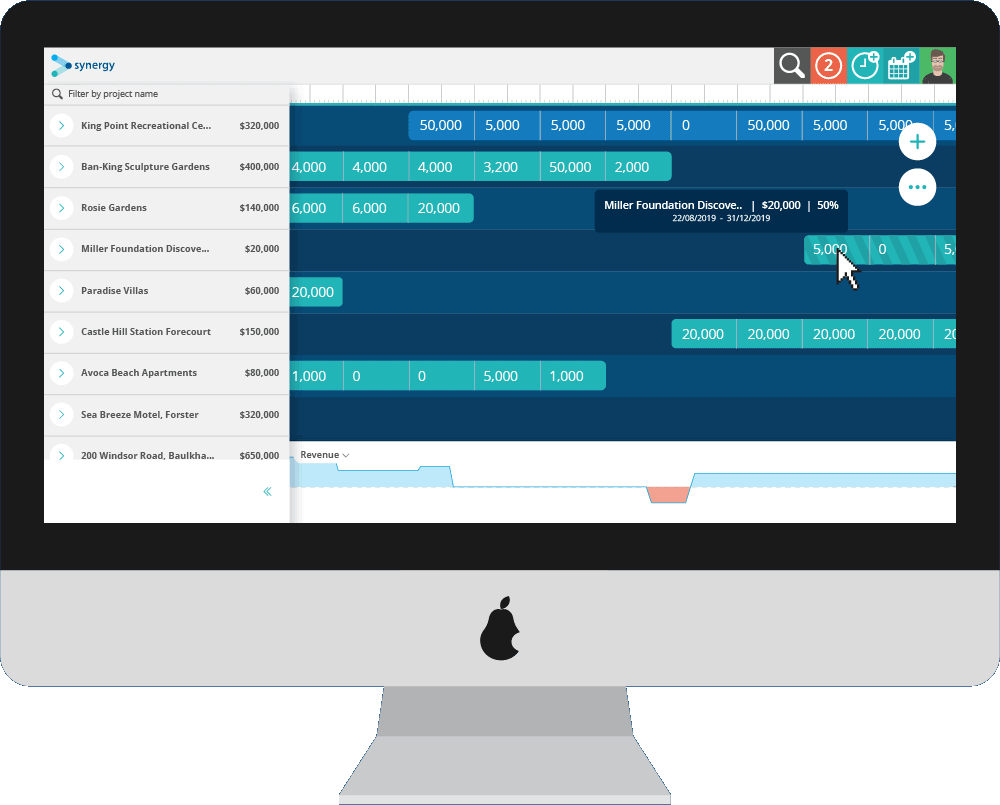
Staffing needs are determined mainly by how the organization has defined its goals and designed the jobs that make up its total workload. How effectively an organization is able to meet those needs, once they are defined, depends on both its staffing processes and the characteristics of the available human resource pool. While manpower planning and management, and the models used in these activities, are important parts of the overall staffing picture, many other factors enter into human resource management, as noted earlier. In this chapter, we concentrate on models for manpower management, that is, for deciding how many workers, of what general types, are needed to staff the organization without regard for specific job characteristics, worker qualifications, or performance standards. In Chapter 4 we discuss these and other considerations that are also important for effective deployment of human resources.
The data used to support these models are derived from a limited sample.It is important to recognize that determining the appropriate number of aviation safety inspectors (ASIs), system-wide or locally, at any given time is by no means a simple matter, since it is dependent on how work is structured and what defines acceptable individual and system performance, as well as the characteristics of the current and projected workforce. An estimation model provides empirically derived formulas to predict effort as a function of LOC or FP. Estimate the cost or effort required for each.©J. Decompose the process into a set of tasks or activities.2. Then compute the expected value: EV = (sopt + 4 sm + spess)/6 4.Īpply baseline productivity metrics to compute estimated cost or effort.©J. Make optimistic (sopt), most likely (sm), and pessimistic (spess) estimates for each item. Based on the software scope, decompose the software into problem functions that can be estimated individually. #Staffing level estimation in software engineering serial number#
Sharpdesk 3.3 Installer Serial Number more. The estimated values will be relatively unaffected by changes to the requirements.©J.

The teams ability to handle the components is well known, and4. Cost or effort required for each component can be accurately estimated,3.
DecompositionDecomposition should be done in such a way that1. Decomposition Techniques To obtain an estimation, we can decompose the problem to be solved, or decompose the process.©J. Three Approaches Estimation can be done by using. Major FactorsMajor factors that influence software cost:. Another Observation Estimation for software project carries inherent risk because of uncertainty in project complexity, project size, and structure (of requirements and problem to be solved).©J. 
An Observation Estimation of resources, cost, and schedule for a software development effort requires experience, access to good historical information, and the courage to commit to quantitative measures when qualitative data are all that exist.©J.
 On Precision It is the mark of an instructed mind to rest satisfied with the degree of precision which the nature of subject admits, and not to seek exactness when only an approximation of the truth is possible. Huang Department of Computer Science University of Houston Houston, TX Breaking down a Project into major Functions or related Software Engineering. Steps in Software Project Estimation are. Boehm, Barry, Software Engineering Economics, Prentice-Hall, 1981. The four basic steps in software project estimation are of people (i.e., an allocated maintenance team) so estimates have to deal with fitting work into a fixed timeframe with a constant staffing level. With the effort estimate (in person-months), it may be tempting to pick any project duration based on convenience and then fix a suitable team size to ensure that the total effort matches the estimate. 4.2 Project Schedule and Staffing After establishing a goal on the effort front, we need to establish the goal for delivery schedule.
On Precision It is the mark of an instructed mind to rest satisfied with the degree of precision which the nature of subject admits, and not to seek exactness when only an approximation of the truth is possible. Huang Department of Computer Science University of Houston Houston, TX Breaking down a Project into major Functions or related Software Engineering. Steps in Software Project Estimation are. Boehm, Barry, Software Engineering Economics, Prentice-Hall, 1981. The four basic steps in software project estimation are of people (i.e., an allocated maintenance team) so estimates have to deal with fitting work into a fixed timeframe with a constant staffing level. With the effort estimate (in person-months), it may be tempting to pick any project duration based on convenience and then fix a suitable team size to ensure that the total effort matches the estimate. 4.2 Project Schedule and Staffing After establishing a goal on the effort front, we need to establish the goal for delivery schedule.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
